 |
Engineers at Georgia Tech have taken advantage of nanotechnology to create a rectenna that captures visible light and converts it into direct current. The rectenna can only absorb microwave energy in the past and convert it into usable electric energy. The idea of ​​capturing visible light and converting it into direct current was previously considered an impractical idea, but advances in carbon nanotubes and microfabrication technology have allowed Georgia Tech engineers to create rectennas that capture and convert light energy into direct current. Researchers believe that their results can ultimately double solar energy collection efficiency.
Rectifying antennas have emerged 40 years ago and have been used for microwave capture and energy conversion. These microwave wavelengths are shorter than 10 microns (in the infrared range) and have been used in near field communications (NFC). However, researchers have been trying to create a rectenna in the visible light band, but with little success.
These advancements have enabled researchers to use chemical vapor deposition on the top of a silicon substrate to cultivate hundreds of billions of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays. These nanotubes use glazed and aluminum oxide insulators, and the entire array is covered with a light-transmissive calcium layer using aluminum as the anode.
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes generate electrical energy by oscillating optical radiation and then pass through built-in rectifiers, in which the alternating current is converted into direct current, which in turn charges the device. These rectifiers turn on and off at an alarming rate, one quadrillion per second, pushing electrons through the outermost electrode to create a small amount of direct current.
Although the current efficiency of these devices is less than one percent, Georgia Tech engineers are working hard to optimize the technology. They believe that they can greatly improve their performance and lead to practical applications in solar energy.
They may eventually double solar cell efficiency and reduce costs by a factor of 10, making it a completely disruptive technology that will change the world.


1. Naipu Pump offers all metal wet parts with high chrome white iron (27% chrome).The high chrome white iron is a very good wear-resistant material and nice wear-resistant is our slurry pumps important character.
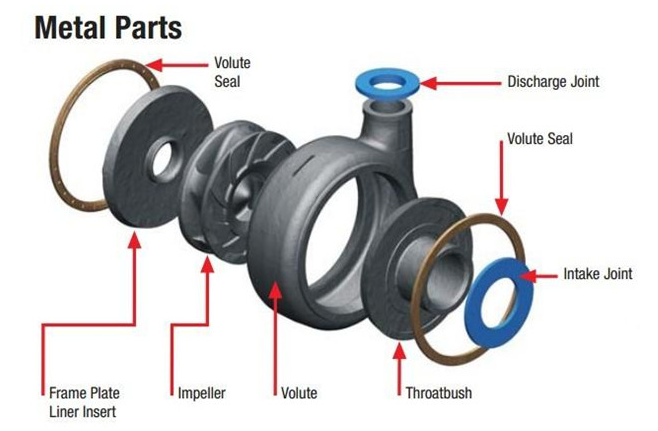
2. Metal Slurry Pump Parts material construction
LINERS
IMPELLER
CASING
BASE
EXPELLER
EXPELLER RING
SHAFT SLEEVE
SEALS
Standard
Chrome Alloy
Chrome Alloy
SG Iron
SG Iron
Chrome Alloy
Chrome Alloy
SG Iron
Rubber
Options
Ferralium
Ferralium
SG Iron
MS
NI Resist
NI Resist
EN56C
Ceramic
Natural Rubber
Natural Rubber
or
SG Iron
or
SG Iron
and
Nitrile
Hastelloy C
316 SS
W151
Polyurethane
Neoprene
Butyl
Viton
Nitrile
EPDM
Hypalon
Hastelloy C
316 SS
W151
Polyurethane
Neoprene
Butyl
Nitrile
Hypalon
Various grades
Fabricated
Cast Iron
Ferralium
Hastelloy C
Polyurethane
316 SS
W151
Ferralium
Hastelloy C
316 SS
Rubber
W151
Polyurethane
Neoprene
Butyl
Nitrile
Ferralium
Hastelloy C
Titanium
316 SS
304 SS
Stellite
Chrome Oxide
Nordel
Neoprene
Viton
Pump Parts,Slurry Pump Metal Parts,Metal Slurry Pump Parts,Slurry Pump Fluid Parts,Slurry Pump Wet Parts
Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com