The research team of the Institute of Physical Research of the University of Tokyo, Tokunaga-shi Institute of History, announced on January 13, 2015 that in cooperation with the Japan Industrial Technology Research Institute, Fukuoka University, Sophia University, and Aoyama Gakuin University, it was discovered in barium ferrite. The new direction of the dielectric polarization component is not known, and it is verified that the polarization of the dielectric can be controlled by the magnetic field. The polarization of the dielectric is different from the original after a magnetic field is applied, and it can be maintained even after the magnetic field is removed. Therefore, it is highly expected to be used as a nonvolatile memory material. Moreover, this effect is still observed at room temperature of 27 degrees Celsius.
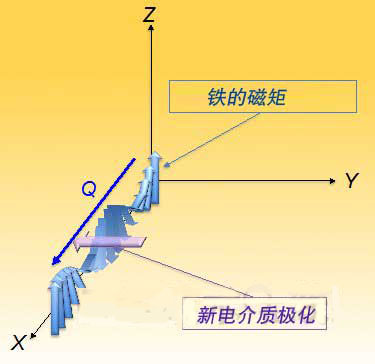
The relation between the magnetic moment and the polarization component of the new dielectric is schematically represented. The X and Z directions are parallel to the crystallized a and c axes, respectively.
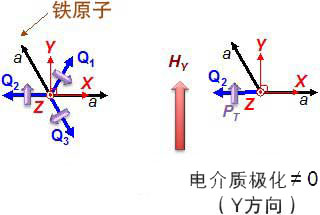
Schematic diagram of polarization alignment in the crystal of barium ferrite
Barium ferrite is a chemical compound of formula BiFeO3. Its crystal structure is similar to that of a representative ferroelectric barium titanate and a manganic oxide known for its enormous magnetoresistance, and has a perovskite structure as its basic structure. As a lead-free ferroelectric body, barium ferrite can have a large polarization state of a self-generating medium, and is in a “multiferroic state†in which a strong dielectric body and a magnet coexist.

Modalized representation of 3-valued storage. By selecting one of the three directions of Q shown above by a magnetic field or an electric field, three states in which the polarization direction of the dielectric changes at 120 degrees can be expressed.
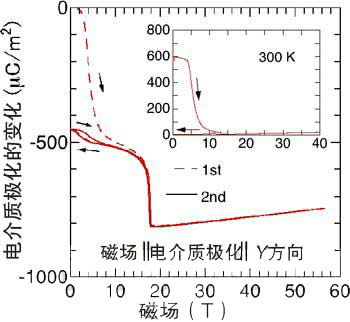
Dielectric polarization magnetic field dependence
Multiferroic substances coexisting with magnetism and ferroelectricity have been investigated as candidates for future low-power memory devices. However, many of the previously discovered multiferroic materials exhibited this characteristic only at minus 200 degrees Celsius, which has become a huge obstacle to practical use. The barium ferrite has attracted attention as a new generation of storage materials because it can work in a multi-iron state at room temperature. However, if it is to be used for storage, it needs to have the property that when the magnetic or dielectric side changes, the other side also changes. This confirmed the phenomenon successfully.
The application of a strong magnetic field to a good single crystal of barium ferrite shows that in addition to the previously known dielectric polarization parallel to the crystalline c-axis, there is dielectric polarization perpendicular to the crystalline c-axis, and this is identified. The new dielectric polarization component can be controlled by the magnetic field. Furthermore, even if a magnetic field of about 1 T can be output after the polarization is applied, the polarization state of the dielectric does not change. This time, the characteristics were changed with a strong magnetic field, but in the future, we will try to use the electric field to control it for practical use. Previous reports and the results of this time have shown the possibility of using electric fields to control. If the control using the electric field is realized, the barium ferrite will be further approached as a target of the storage material. (Reporter: Middle truth)
Pedestrian Street Light Head,Solar Integrated Street Light,Waterproof Solar Integrated Street Light,Stylish Street Light
Jiangsu chuanglv Transportation Facilities Co., Ltd , https://www.clsolarlights.com